The trajectory of artificial intelligence development has long been marked by a peculiar paradox: as language models grew more sophisticated in their analytical capabilities, they remained conspicuously artificial in their communication patterns. This "AI voice" - characterized by rigid structures, predictable transitions, and an almost algorithmic approach to language - has persisted as a subtle but unmistakable barrier between artificial and human intelligence.
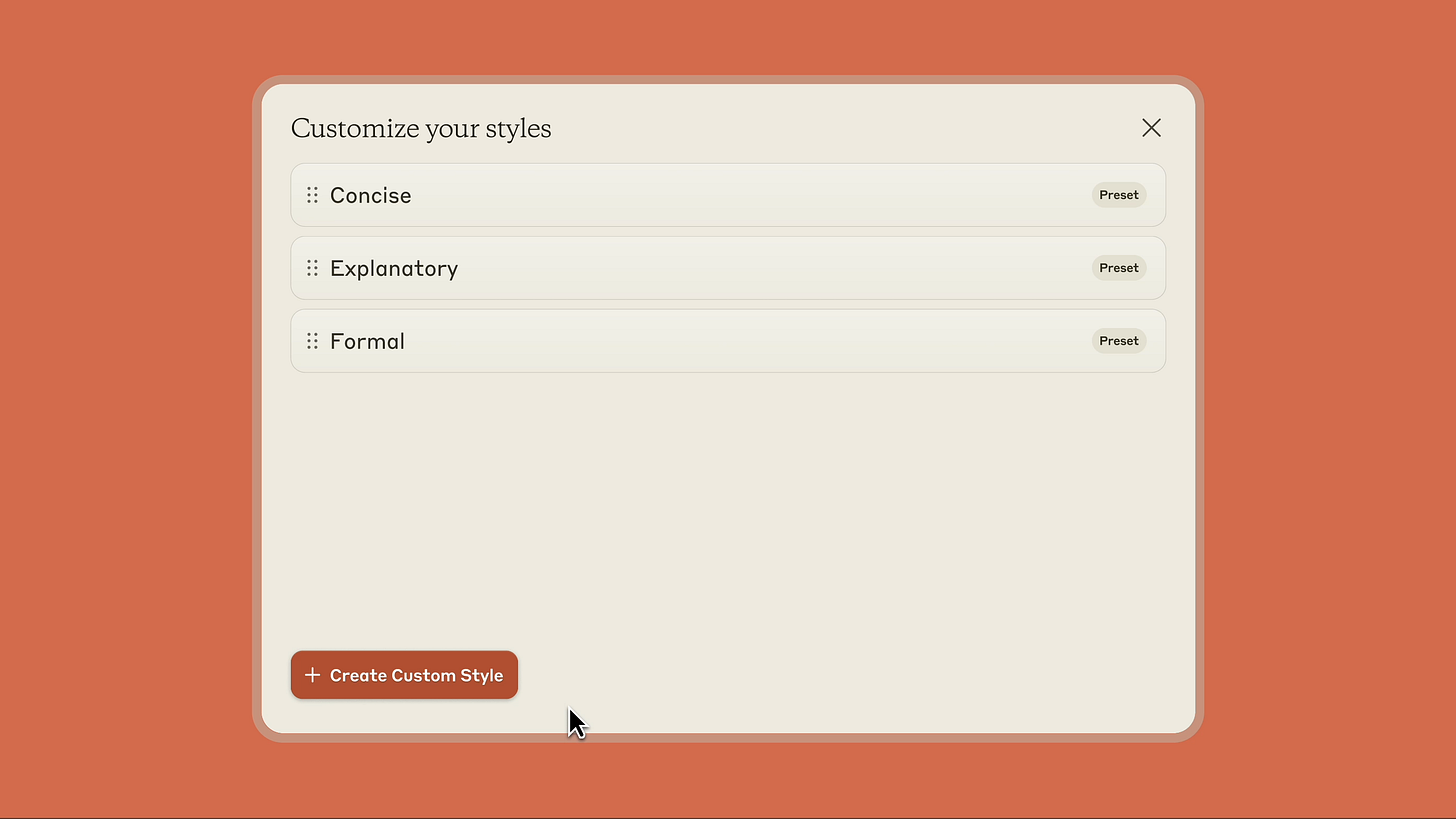
Anthropic's recent introduction of custom writing styles for Claude represents a significant shift in addressing this challenge. The system now allows users to upload their own writing samples to create personalized communication patterns, while also offering preset styles like formal, concise, and explanatory. This capability moves beyond simple tone adjustments, instead analyzing and adopting the deeper structural patterns that make each writer's voice unique.
Understanding this evolution requires examining the fundamental architecture of traditional language models. These systems, while remarkably capable of processing and generating content, have historically operated within rigid frameworks that prioritize technical accuracy over authentic communication patterns. The result has been a form of digital uncanny valley - outputs that are undeniably competent but lacking the natural variation and contextual awareness that characterizes human communication.
Content creators and content-heavy enterprises often spend a considerable amount of time editing AI content when it is used, primarily dedicated to humanizing the output. This efficiency gap highlights a critical limitation in the practical application of AI language models, particularly in professional contexts where authenticity and brand voice consistency are paramount.
The introduction of custom writing styles in language models like Claude represents more than an incremental improvement - it signals a fundamental shift in how we conceptualize AI communication. By moving beyond the traditional paradigm of predetermined response patterns, this development addresses a core challenge in human-AI interaction: the ability to maintain technical precision while adapting to diverse communication contexts.
This evolution is particularly significant when viewed through the lens of historical AI development:
First Generation: Rule-based responses with minimal flexibility
Second Generation: Neural networks capable of generating coherent but rigid content
Third Generation: Large language models with improved contextual understanding
Current Innovation: Adaptive systems capable of personalized communication patterns
The implications of this progression extend far beyond mere stylistic improvements. As AI systems begin to understand and replicate nuanced communication patterns, we're witnessing the emergence of a new paradigm in human-AI interaction - one where artificial intelligence can maintain its computational advantages while adopting more natural, context-appropriate communication styles.
However, this advancement also raises important questions about the nature of authentic communication and the role of AI in content creation. As these systems become more adept at mimicking human writing patterns, the distinction between AI-generated and human-authored content becomes increasingly nuanced, necessitating a deeper examination of how we evaluate and utilize AI communication tools.
What's particularly compelling about this development is its potential to democratize advanced content creation. By reducing the post-processing overhead traditionally associated with AI-generated content, these adaptable systems could significantly lower the barriers to entry for organizations seeking to scale their content operations while maintaining consistent voice and quality.
Beyond Simple Tone Adjustment
The technical architecture behind Claude's custom writing styles represents a significant departure from traditional approaches to AI communication. While previous systems relied on superficial tone adjustments - essentially applying preset filters to standardized outputs - Claude's implementation leverages sophisticated pattern recognition algorithms that analyze writing at multiple structural levels.
At its core, the system employs what could be termed "communication fingerprinting" - a complex analysis framework that examines not just vocabulary and sentence structure, but the underlying patterns that make individual writing styles distinctive. This includes analyzing argument construction methodologies, transition mechanisms, and even subtle markers like parenthetical usage patterns or technical depth calibration.
What makes this particularly noteworthy is the system's ability to maintain semantic integrity while adapting stylistic elements. Unlike simpler implementations that might compromise meaning in pursuit of style matching, Claude's architecture appears to create a clear separation between content generation and style application layers. This architectural decision allows for more nuanced adaptation while preserving the intended message's clarity and accuracy.
This advancement builds upon recent developments in natural language processing, but introduces several key innovations:
Pattern recognition that operates at multiple abstraction levels simultaneously
Dynamic style adaptation that maintains contextual awareness
Integration with existing language model capabilities without compromising core functionality
Real-world Applications & Impact
The practical implications of this technology extend far beyond simple content generation. Early implementations reveal three primary domains where custom writing styles are fundamentally altering workflows:
Enterprise Content Scaling: Organizations can maintain consistent brand voice across massive content operations without the traditional overhead of extensive human editing.
Professional Communications: The ability to maintain consistent communication styles across different contexts is particularly valuable in client-facing roles. Law firms and consulting agencies can use these capabilities to ensure client communications maintain appropriate formality and terminology while preserving their distinctive professional voice.
Educational Content Development: Educational institutions can leverage these capabilities to create adaptive learning materials that maintain consistent pedagogical approaches while adjusting technical depth and explanation styles based on student needs.
What's particularly significant about these applications is their scalability. Unlike previous attempts at style matching, which often broke down as content volume increased, these new systems appear to maintain consistency even across large-scale content operations. This suggests the underlying pattern recognition mechanisms are both robust and computationally efficient.
The technology also addresses a long-standing challenge in AI content generation: the reduction of what industry professionals term "AI artifacts" - those subtle but noticeable markers that identify content as machine-generated. By analyzing and replicating deeper structural patterns in writing, the system produces output that integrates more naturally with human-generated content.
Perhaps most intriguingly, early adopters will find an unexpected benefit: the system's analysis of writing patterns often reveals insights about their own communication styles that they weren't consciously aware of. This meta-analysis capability could have interesting implications for professional development and communication training.
The Bottom Line
Claude's custom writing styles mark a pivotal moment in AI development, fundamentally changing how AI adapts to human communication patterns. By enabling sophisticated pattern recognition and style replication, this technology addresses one of the most persistent challenges in AI-assisted content creation: the substantial time investment required to "humanize" machine-generated content.
The implications extend beyond mere stylistic improvements. This advancement provides a foundation for scalable, personalized communication across enterprises while maintaining authenticity and brand consistency. Early implementations demonstrate significant reductions in editing overhead while improving content quality - a combination that has proven elusive in previous AI systems.
Looking ahead, this development likely represents the beginning of a broader evolution in AI communication capabilities. The underlying architecture, with its multi-layered pattern recognition and dynamic adaptation mechanisms, establishes a technical foundation for even more sophisticated human-AI interaction patterns.
However, the unprecedented degree of autonomy in content creation raises critical concerns. As AI becomes more adept at mirroring human communication styles, it introduces the risk of blurring the lines between human and machine-generated content. This can lead to challenges in accountability, as it may become increasingly difficult to attribute authorship or verify the intent behind a piece of content. Furthermore, misuse of this technology could facilitate the spread of misinformation or deceptive practices on an unprecedented scale, as AI systems can convincingly adopt authoritative or trustworthy tones.
Another significant risk is the potential to dissuade human verification and foster excessive reliance on LLMs with reduced supervision. The convenience and perceived reliability of such systems may lead to a diminished role for human oversight, increasing the likelihood of errors or ethical lapses going unnoticed. This reliance could, in turn, erode critical thinking and editorial diligence, leaving enterprises vulnerable to unintended consequences.
The critical question now shifts from whether AI can generate coherent content to how seamlessly it can enhance human communication while maintaining authenticity and purpose. Equally important, however, is ensuring that robust safeguards are in place to manage the ethical and practical risks of such advancements. Striking this balance—between leveraging the potential of autonomous AI content creation and mitigating its inherent risks—may well define the next era of AI-assisted communication.
Keep a lookout for the next edition of AI Uncovered!
Follow on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram for more AI-related content.